How do I use a diffable data source?
Asked on 2024-07-31
1 search
To use a diffable data source, you can follow these steps:
-
Create a Data Source: Initialize a diffable data source with a table view or collection view. This data source will manage the data and provide the necessary updates to the UI.
-
Define Snapshots: Use snapshots to represent the current state of your data. A snapshot is a lightweight representation of your data that you can apply to the data source to update the UI.
-
Apply Snapshots: Apply the snapshot to the data source. The diffable data source will automatically calculate the differences and update the UI accordingly.
Here is a basic example in Swift:
import UIKit
class MyViewController: UIViewController {
var tableView: UITableView!
var dataSource: UITableViewDiffableDataSource<Section, Item>!
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
tableView = UITableView(frame: view.bounds)
view.addSubview(tableView)
// Initialize the data source
dataSource = UITableViewDiffableDataSource<Section, Item>(tableView: tableView) { (tableView, indexPath, item) -> UITableViewCell? in
let cell = tableView.dequeueReusableCell(withIdentifier: "cell", for: indexPath)
cell.textLabel?.text = item.title
return cell
}
// Create and apply a snapshot
var snapshot = NSDiffableDataSourceSnapshot<Section, Item>()
snapshot.appendSections([.main])
snapshot.appendItems([Item(title: "Item 1"), Item(title: "Item 2")])
dataSource.apply(snapshot, animatingDifferences: true)
}
}
enum Section {
case main
}
struct Item: Hashable {
let title: String
}
In this example:
Sectionis an enum representing the sections in the table view.Itemis a struct representing the items in the table view.UITableViewDiffableDataSourceis used to manage the data and provide updates to the table view.
For more detailed information and advanced usage, you can refer to the session Track model changes with SwiftData history which covers transactions and changes, including how to handle data updates efficiently.
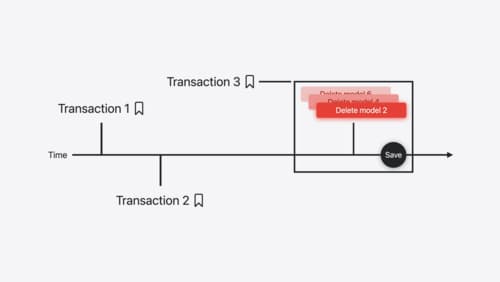
Track model changes with SwiftData history
Reveal the history of your model’s changes with SwiftData! Use the history API to understand when data store changes occurred, and learn how to use this information to build features like remote server sync and out-of-process change handing in your app. We’ll also cover how you can build support for the history API into a custom data store.

What’s new in SwiftData
SwiftData makes it easy to add persistence to your app with its expressive, declarative API. Learn about refinements to SwiftData, including compound uniqueness constraints, faster queries with #Index, queries in Xcode previews, and rich predicate expressions. Join us to explore how you can use all of these features to express richer models and improve performance in your app. To discover how to build a custom data store or use the history API in SwiftData, watch “Create a custom data store with SwiftData” and “Track model changes with SwiftData history”.
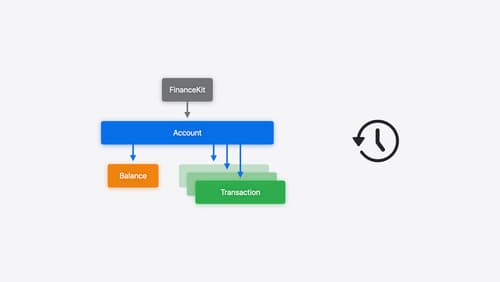
Meet FinanceKit
Learn how FinanceKit lets your financial management apps seamlessly and securely share on-device data from Apple Cash, Apple Card, and more, with user consent and control. Find out how to request one-time and ongoing access to accounts, transactions, and balances — and how to build great experiences for iOS and iPadOS.
