How to use pointers
Asked on 2024-08-01
1 search
To use pointers in Swift, you can refer to the session titled "Explore Swift performance" from WWDC 2024. Here are some key points discussed in the session:
-
Memory Representation:
- Every value in Swift has a type, and the type dictates how the value is represented in memory, including its inline representation.
- The context of the value dictates where the memory comes from to hold that inline representation. For example, arrays and dictionaries contain all their elements via their buffer.
-
Types of References:
- There are different types of references in Swift, such as strong references, weak and unowned references, unmanaged references, and uncertain or conservative references. These references help manage memory and ownership in Swift.
-
Borrowing Values:
- Borrowing a value means asserting that nobody else can consume or mutate it. This is useful when you just want to read a value without changing it.
-
Buffer Size:
- Swift uses an arbitrary buffer size of three pointers. If the value stored in a protocol type can fit into that buffer, Swift will put it there. Otherwise, it allocates space for the value on the heap and stores that pointer in the buffer.
For more detailed information, you can watch the session Explore Swift performance starting at 11:57.
Relevant Sessions
If you have any specific questions or need further details, feel free to ask!
Xcode essentials
Edit, debug, commit, repeat. Explore the suite of tools in Xcode that help you iterate quickly when developing apps. Discover tips and tricks to help optimize and boost your development workflow.
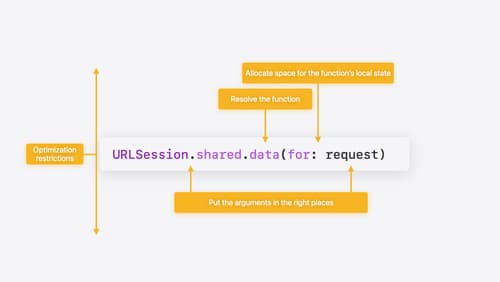
Explore Swift performance
Discover how Swift balances abstraction and performance. Learn what elements of performance to consider and how the Swift optimizer affects them. Explore the different features of Swift and how they’re implemented to further understand the tradeoffs available that can impact performance.

Analyze heap memory
Dive into the basis for your app’s dynamic memory: the heap! Explore how to use Instruments and Xcode to measure, analyze, and fix common heap issues. We’ll also cover some techniques and best practices for diagnosing transient growth, persistent growth, and leaks in your app.
