how do I create a core data instance and use my own DB backend?
Asked on 2024-08-02
1 search
To create a Core Data instance and use your own database backend with SwiftData, you can follow these steps:
-
Create a Custom Data Store:
- Implement a custom data store by conforming to the new
Datastoreprotocol. This protocol defines all the necessary functionality for the store to be usable by the model context, including save, fetch, and caching operations. - For example, you can create a custom data store that uses JSON files for persistence.
- Implement a custom data store by conforming to the new
-
Configure the Model Container:
- Instead of using the default model container, you can create a custom model container configuration. This allows you to specify the URL of the data on disk and other properties.
- Use the
containerproperty in the properties closure to create a configuration for your model and pass the schema.
-
Adopt the Custom Data Store:
- Replace the default model configuration with the custom data store configuration in your app definition. This tells the model container to use the custom store type without requiring changes to the model or view code.
Here are some relevant sessions and timestamps that provide more details on these steps:
- What’s new in SwiftData (04:29): Discusses how to customize the model container and use custom data stores.
- Create a custom data store with SwiftData (00:37): Introduces custom data stores and how to use them with SwiftData.
- Create a custom data store with SwiftData (05:40): Explains the Datastore protocol and how to implement a custom data store.
Relevant Sessions
- What’s new in SwiftData
- Create a custom data store with SwiftData
- Track model changes with SwiftData history
By following these steps and referring to the mentioned sessions, you can create a Core Data instance and use your own database backend with SwiftData.

What’s new in SwiftData
SwiftData makes it easy to add persistence to your app with its expressive, declarative API. Learn about refinements to SwiftData, including compound uniqueness constraints, faster queries with #Index, queries in Xcode previews, and rich predicate expressions. Join us to explore how you can use all of these features to express richer models and improve performance in your app. To discover how to build a custom data store or use the history API in SwiftData, watch “Create a custom data store with SwiftData” and “Track model changes with SwiftData history”.
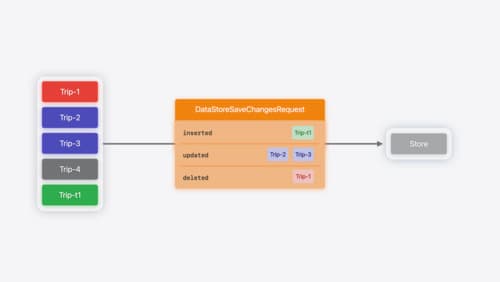
Create a custom data store with SwiftData
Combine the power of SwiftData’s expressive, declarative modeling API with your own persistence backend. Learn how to build a custom data store and explore how to progressively add persistence features in your app. To get the most out of this session, watch “Meet SwiftData” and “Model your schema with SwiftData” from WWDC23.
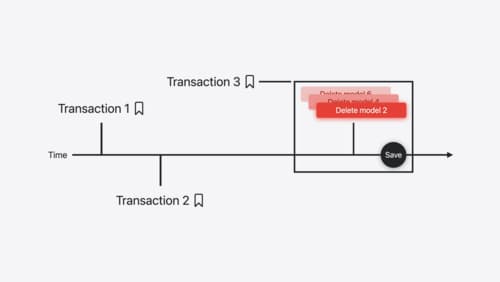
Track model changes with SwiftData history
Reveal the history of your model’s changes with SwiftData! Use the history API to understand when data store changes occurred, and learn how to use this information to build features like remote server sync and out-of-process change handing in your app. We’ll also cover how you can build support for the history API into a custom data store.
