sendable
Asked on 2024-08-03
4 searches
The concept of "sendable" in Swift is discussed in the context of ensuring data-race safety when working with concurrency. In Swift 6, the language requires that values shared between concurrency domains be sendable. A sendable value is one that protects its state from concurrent accesses, which is crucial for avoiding data races that can lead to crashes or unpredictable behavior.
Here are some key points about sendable from the sessions:
-
Explicit Sendable Conformance for Public Types:
- Swift does not infer sendability for public types automatically. This is because marking a type as sendable is a guarantee to your clients that the type contains no mutable state. Therefore, you need to explicitly add sendable conformances on public types.
- Example: In the session Migrate your app to Swift 6, it is explained that for a public type shared outside a module, you need to explicitly mark it as sendable to avoid multiple warnings.
-
Data-Race Safety Verification:
- In Swift 6, the data-race safety of your program is fully verified at compile time. This is achieved by requiring that values shared between concurrency domains are sendable.
- Example: The session A Swift Tour: Explore Swift’s features and design discusses how sendable values protect their state from concurrent accesses, and how actors can be used to encapsulate shared mutable state safely.
-
Handling Non-Sendable Types:
- If a type cannot be made sendable (e.g., an Objective-C type that stores mutable state), you may need to make choices about safety, such as reasoning about the type's usage or adding synchronization manually.
- Example: The session Migrate your app to Swift 6 covers scenarios where a type cannot be marked as sendable and the considerations that need to be made.
Relevant Sessions
These sessions provide a comprehensive overview of how to handle sendable types in Swift 6 and ensure data-race safety in your applications.
A Swift Tour: Explore Swift’s features and design
Learn the essential features and design philosophy of the Swift programming language. We’ll explore how to model data, handle errors, use protocols, write concurrent code, and more while building up a Swift package that has a library, an HTTP server, and a command line client. Whether you’re just beginning your Swift journey or have been with us from the start, this talk will help you get the most out of the language.

What’s new in App Intents
Learn about improvements and all-new features with App Intents, and discover how this framework can help you expose your app’s functionality to Siri, Spotlight, Shortcuts, and more. We’ll show you how to make your entities more meaningful to the platform with the Transferable API, File Representations, new IntentFile APIs, and Spotlight Indexing, opening up powerful functionality in Siri and the Shortcuts app. Empower your intents to take people deep into your app with URL Representable Entities. Explore new techniques to model your entities and intents with new APIs for error handling and union values.
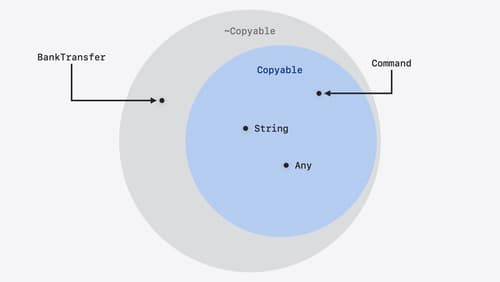
Consume noncopyable types in Swift
Get started with noncopyable types in Swift. Discover what copying means in Swift, when you might want to use a noncopyable type, and how value ownership lets you state your intentions clearly.
