using ModelActor in swiftdata
Asked on 2024-08-03
1 search
To use ModelActor in SwiftData, you can leverage the actor model in Swift to ensure safe concurrent access to your data. Here are some key points from the WWDC sessions that can help you understand how to use actors and SwiftData together:
-
Actors in Swift:
- Actors are reference types that encapsulate shared mutable state and automatically protect their state by serializing accesses. Only a single task is allowed to execute at a time on an actor, and calls to actor methods from outside the context of the actor are asynchronous. This helps in avoiding data races and ensuring thread safety.
- For example, you can make concurrent accesses to a user store safe by making it an actor. This way, accesses are synchronized, and you can use the
awaitkeyword to handle asynchronous access from different concurrency domains (A Swift Tour: Explore Swift’s features and design).
-
SwiftData Framework:
- SwiftData is a framework that makes it easy to build your app's model layer and persist it across launches. It provides persistence, modeling, migration of your schema, graph management, and synchronization with CloudKit.
- You can define your schema with just a few additions to a normal Swift class by applying the model macro. This allows you to specify behaviors on properties and relationships to describe how models relate to one another (Platforms State of the Union).
-
Concurrency and Data Safety:
- When migrating to Swift 6, you can use actors to manage concurrency. For instance, you can have UIViews and models run on the main actor, while background operations are performed on dedicated actors. This setup helps in avoiding data races by ensuring that shared mutable state is not accessed simultaneously by multiple actors (Migrate your app to Swift 6).
-
Custom Data Stores:
- SwiftData allows you to create custom data stores by changing the data store configuration. You can implement support for any persistence backend using the new datastore protocol. This flexibility opens up a range of possibilities for using different storage backends like SQLite, remote web services, or even JSON files (Create a custom data store with SwiftData).
For more detailed information, you can refer to the following sessions:
- A Swift Tour: Explore Swift’s features and design
- Platforms State of the Union
- Migrate your app to Swift 6
- Create a custom data store with SwiftData
These sessions provide a comprehensive overview of how to use actors in Swift and integrate them with SwiftData for safe and efficient data management.
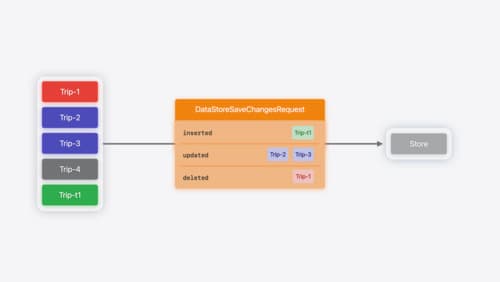
Create a custom data store with SwiftData
Combine the power of SwiftData’s expressive, declarative modeling API with your own persistence backend. Learn how to build a custom data store and explore how to progressively add persistence features in your app. To get the most out of this session, watch “Meet SwiftData” and “Model your schema with SwiftData” from WWDC23.
A Swift Tour: Explore Swift’s features and design
Learn the essential features and design philosophy of the Swift programming language. We’ll explore how to model data, handle errors, use protocols, write concurrent code, and more while building up a Swift package that has a library, an HTTP server, and a command line client. Whether you’re just beginning your Swift journey or have been with us from the start, this talk will help you get the most out of the language.

What’s new in SwiftData
SwiftData makes it easy to add persistence to your app with its expressive, declarative API. Learn about refinements to SwiftData, including compound uniqueness constraints, faster queries with #Index, queries in Xcode previews, and rich predicate expressions. Join us to explore how you can use all of these features to express richer models and improve performance in your app. To discover how to build a custom data store or use the history API in SwiftData, watch “Create a custom data store with SwiftData” and “Track model changes with SwiftData history”.
