swift concurrency actor
Asked on 2024-08-05
1 search
Actors in Swift are a powerful feature designed to help manage concurrency and ensure data-race safety. Here are some key points about actors from the WWDC sessions:
-
Definition and Purpose:
- Actors are similar to classes in that they are reference types that can encapsulate shared mutable state. However, actors automatically protect their state by serializing accesses, ensuring that only a single task can execute at a time on an actor (A Swift Tour: Explore Swift’s features and design).
-
Concurrency and Data-Race Safety:
- Swift 6 introduces complete data-race protection, which is fully verified at compile time. This is achieved by requiring that values shared between concurrency domains are sendable. Actors play a crucial role in this by ensuring that accesses to their state are synchronized (A Swift Tour: Explore Swift’s features and design).
- The Swift 6 language mode enforces data isolation, preventing accidental sharing of state between tasks and actors. This helps in refactoring or adding new functionality without introducing concurrency bugs (Migrate your app to Swift 6).
-
Usage in Code:
- When accessing an actor from a different concurrency domain, the access is asynchronous, and the
awaitkeyword is used. This ensures that the access is properly synchronized and safe from data races (A Swift Tour: Explore Swift’s features and design). - In scenarios where you need to ensure that a method is called on a specific actor, such as the main actor, you can use the
assume isolatedmethod. This method tells Swift that the code is already running on the specified actor, providing a way to enforce concurrency guarantees (Migrate your app to Swift 6).
- When accessing an actor from a different concurrency domain, the access is asynchronous, and the
Relevant Sessions
These sessions provide a comprehensive overview of how actors are used in Swift to manage concurrency and ensure data-race safety.
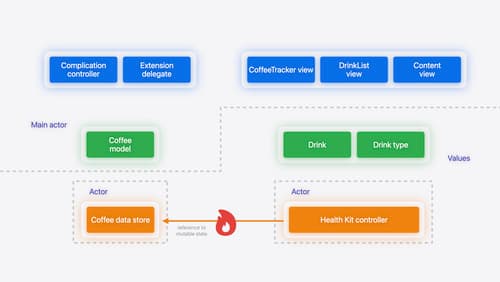
Migrate your app to Swift 6
Experience Swift 6 migration in action as we update an existing sample app. Learn how to migrate incrementally, module by module, and how the compiler helps you identify code that’s at risk of data races. Discover different techniques for ensuring clear isolation boundaries and eliminating concurrent access to shared mutable state.
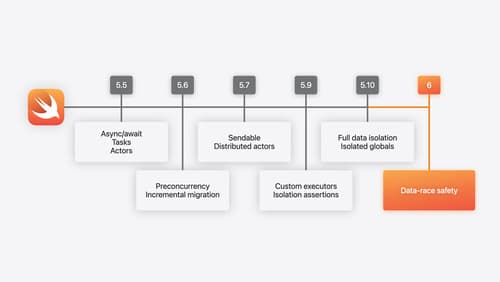
What’s new in Swift
Join us for an update on Swift. We’ll briefly go through a history of Swift over the past decade, and show you how the community has grown through workgroups, expanded the package ecosystem, and increased platform support. We’ll introduce you to a new language mode that achieves data-race safety by default, and a language subset that lets you run Swift on highly constrained systems. We’ll also explore some language updates including noncopyable types, typed throws, and improved C++ interoperability.
A Swift Tour: Explore Swift’s features and design
Learn the essential features and design philosophy of the Swift programming language. We’ll explore how to model data, handle errors, use protocols, write concurrent code, and more while building up a Swift package that has a library, an HTTP server, and a command line client. Whether you’re just beginning your Swift journey or have been with us from the start, this talk will help you get the most out of the language.
