what is isolation in swift
Asked on 2024-08-05
1 search
Isolation in Swift, particularly in the context of Swift concurrency, refers to the concept of ensuring that certain pieces of code or data are accessed in a controlled and safe manner to prevent data races and other concurrency issues. Here are some key points about isolation in Swift:
-
Actor Isolation: Swift uses actors to provide isolation. An actor ensures that its state is only accessed by a single thread at a time, preventing data races. For example, marking a delegate as isolated to the main actor ensures that all its methods and property accesses are made on the main thread.
-
Non-Isolated: If a callback or method does not specify how it is called back, it is considered non-isolated. This means it cannot access data that requires a certain isolation. For instance, a method on a main actor isolated type can be declared as non-isolated if it should not be isolated to the main actor.
-
Assume Isolated: This is a way to tell Swift that a piece of code is already running on a specific actor, such as the main actor, without starting a new task. This can be useful when you know for certain that a call will be on a particular actor.
-
Non-Isolated Unsafe: This keyword can be used as a last resort to mark a variable or method as non-isolated, putting the burden on the developer to ensure safety. This should be avoided if possible, as it bypasses Swift's compile-time guarantees.
-
Data Isolation in Swift 6: Swift 6 introduces full enforcement of data isolation, preventing accidental sharing of state between tasks and actors. This helps in catching concurrency bugs at compile time, significantly improving the quality of the app.
For more detailed information, you can refer to the session "Migrate your app to Swift 6" (08:58) and "What’s new in Swift" (28:00).
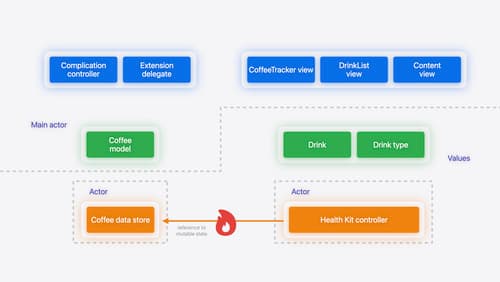
Migrate your app to Swift 6
Experience Swift 6 migration in action as we update an existing sample app. Learn how to migrate incrementally, module by module, and how the compiler helps you identify code that’s at risk of data races. Discover different techniques for ensuring clear isolation boundaries and eliminating concurrent access to shared mutable state.
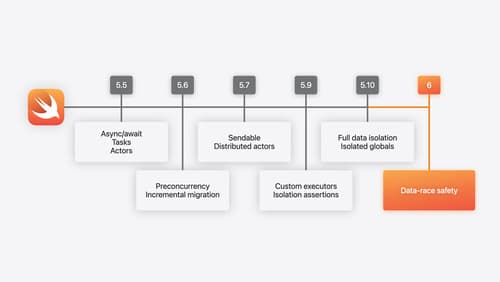
What’s new in Swift
Join us for an update on Swift. We’ll briefly go through a history of Swift over the past decade, and show you how the community has grown through workgroups, expanded the package ecosystem, and increased platform support. We’ll introduce you to a new language mode that achieves data-race safety by default, and a language subset that lets you run Swift on highly constrained systems. We’ll also explore some language updates including noncopyable types, typed throws, and improved C++ interoperability.
