why consuming and borrowing can be applied only to escaping closures?
Asked on 2024-08-09
1 search
Consuming and borrowing can be applied only to escaping closures because of the way Swift manages the lifetime and memory of captured variables in closures.
For non-escaping closures, the closure is guaranteed to be used only within the duration of the call, so the context can be allocated on the stack, and the address of that will be passed to the function. This allows for efficient memory management and ensures that the variable's lifetime is tightly controlled.
However, for escaping closures, the closure can outlive the function call, meaning the context object must be heap allocated and managed with retains and releases. This is because the closure might be used at any point in the future, and Swift needs to ensure that the captured variables remain valid for the entire lifetime of the closure. This is why consuming and borrowing, which involve transferring or temporarily taking ownership of a value, are only applicable to escaping closures. The context essentially behaves like an instance of an anonymous Swift class, and Swift needs to manage the memory and lifetime of these captured variables carefully.
For more details, you can refer to the session Explore Swift performance (28:18).
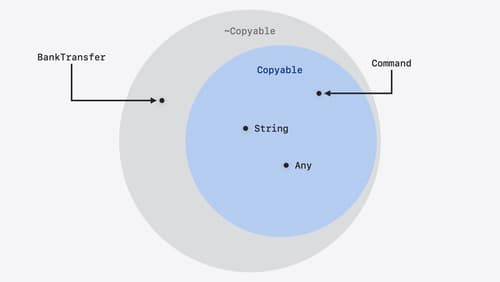
Consume noncopyable types in Swift
Get started with noncopyable types in Swift. Discover what copying means in Swift, when you might want to use a noncopyable type, and how value ownership lets you state your intentions clearly.
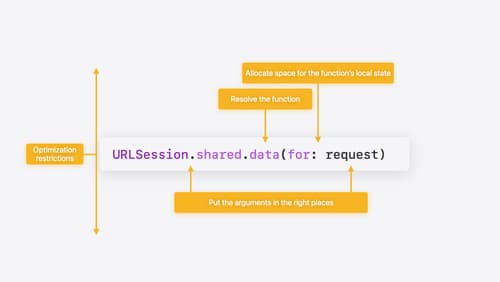
Explore Swift performance
Discover how Swift balances abstraction and performance. Learn what elements of performance to consider and how the Swift optimizer affects them. Explore the different features of Swift and how they’re implemented to further understand the tradeoffs available that can impact performance.

Analyze heap memory
Dive into the basis for your app’s dynamic memory: the heap! Explore how to use Instruments and Xcode to measure, analyze, and fix common heap issues. We’ll also cover some techniques and best practices for diagnosing transient growth, persistent growth, and leaks in your app.
