how reference type is capture in a closure and the changes of the value type are observed?
Asked on 2024-08-09
1 search
In Swift, when you refer to a local variable in a closure, you capture that variable by reference. This allows changes to the variable to be observed in the original scope and vice versa. If the variable is captured by a non-escaping closure, it doesn't change the lifetime of the variable. The closure can handle this by just capturing a pointer to the variable's allocation.
However, if the variable is captured by an escaping closure, the lifetime of the variable can be extended for as long as the closure is alive. As a result, the variable also has to be heap allocated, and the closure context has to retain a reference to that object. This is because escaping closures can outlive the scope in which they were created, necessitating the use of heap allocation to manage the variable's lifetime.
For more details, you can refer to the session Explore Swift performance (28:18).
Relevant Sessions
A Swift Tour: Explore Swift’s features and design
Learn the essential features and design philosophy of the Swift programming language. We’ll explore how to model data, handle errors, use protocols, write concurrent code, and more while building up a Swift package that has a library, an HTTP server, and a command line client. Whether you’re just beginning your Swift journey or have been with us from the start, this talk will help you get the most out of the language.
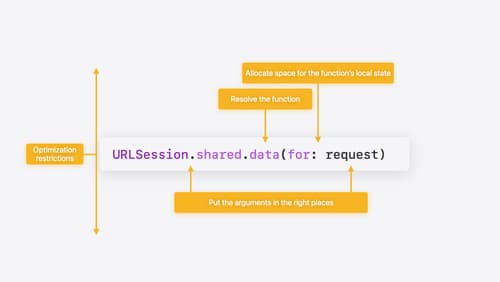
Explore Swift performance
Discover how Swift balances abstraction and performance. Learn what elements of performance to consider and how the Swift optimizer affects them. Explore the different features of Swift and how they’re implemented to further understand the tradeoffs available that can impact performance.

Analyze heap memory
Dive into the basis for your app’s dynamic memory: the heap! Explore how to use Instruments and Xcode to measure, analyze, and fix common heap issues. We’ll also cover some techniques and best practices for diagnosing transient growth, persistent growth, and leaks in your app.
