explain different types of memory (global, stack, heap) and their trade-offs, different performance characteristics
Asked on 2024-08-09
1 search
Types of Memory: Global, Stack, and Heap
Global Memory
- Characteristics:
- Allocated and initialized when the program is loaded.
- Lives for the entire duration of the program.
- Suitable for global variables and static member variables.
- Performance:
- Very cheap in terms of allocation and deallocation.
- Limited to specific patterns due to its fixed lifetime.
Stack Memory
- Characteristics:
- Used for local variables within functions.
- Memory is allocated and deallocated in a last-in, first-out manner.
- Scoped to the function call, meaning it is automatically freed when the function exits.
- Performance:
- Extremely cheap and fast to allocate and deallocate.
- Limited to patterns where the memory usage is scoped to function calls.
Heap Memory
- Characteristics:
- Used for dynamic memory allocation.
- Memory can be allocated and deallocated at arbitrary times.
- Suitable for objects that need to live beyond the scope of a single function call.
- Performance:
- More expensive to allocate and deallocate compared to global and stack memory.
- Flexible but can lead to memory fragmentation and requires manual management or garbage collection.
Trade-offs and Performance Characteristics
-
Global Memory:
- Pros: Minimal overhead, simple to use for static data.
- Cons: Not flexible, can lead to higher memory usage if not managed properly.
-
Stack Memory:
- Pros: Very fast allocation and deallocation, automatic memory management.
- Cons: Limited to function scope, not suitable for data that needs to persist beyond function calls.
-
Heap Memory:
- Pros: Highly flexible, suitable for dynamic and long-lived data.
- Cons: Higher overhead for allocation and deallocation, potential for memory leaks and fragmentation.
For more detailed information, you can refer to the sessions from WWDC:
- Explore Swift performance (Memory allocation)
- Analyze heap memory (Heap memory overview)
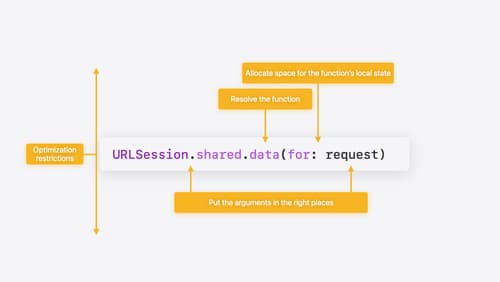
Explore Swift performance
Discover how Swift balances abstraction and performance. Learn what elements of performance to consider and how the Swift optimizer affects them. Explore the different features of Swift and how they’re implemented to further understand the tradeoffs available that can impact performance.

Analyze heap memory
Dive into the basis for your app’s dynamic memory: the heap! Explore how to use Instruments and Xcode to measure, analyze, and fix common heap issues. We’ll also cover some techniques and best practices for diagnosing transient growth, persistent growth, and leaks in your app.
