how to write Pythagorean theorem in swift?
Asked on 2024-08-22
1 search
To write the Pythagorean theorem in Swift, you can use a simple function that calculates the hypotenuse of a right triangle given the lengths of the other two sides. Here's a basic example:
import Foundation
func calculateHypotenuse(a: Double, b: Double) -> Double {
return sqrt(a * a + b * b)
}
let sideA = 3.0
let sideB = 4.0
let hypotenuse = calculateHypotenuse(a: sideA, b: sideB)
print("The hypotenuse is \(hypotenuse)")
This function uses the sqrt function from the Foundation framework to calculate the square root, which is necessary for computing the hypotenuse according to the Pythagorean theorem: ( c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} ).
If you're interested in learning more about Swift's features and design, you might find the session A Swift Tour: Explore Swift’s features and design helpful.

Swift Charts: Vectorized and function plots
The plot thickens! Learn how to render beautiful charts representing math functions and extensive datasets using function and vectorized plots in your app. Whether you’re looking to display functions common in aerodynamics, magnetism, and higher order field theory, or create large interactive heat maps, Swift Charts has you covered.
A Swift Tour: Explore Swift’s features and design
Learn the essential features and design philosophy of the Swift programming language. We’ll explore how to model data, handle errors, use protocols, write concurrent code, and more while building up a Swift package that has a library, an HTTP server, and a command line client. Whether you’re just beginning your Swift journey or have been with us from the start, this talk will help you get the most out of the language.
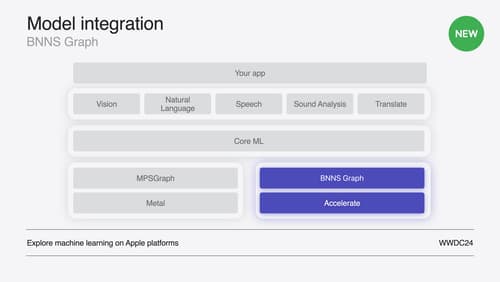
Support real-time ML inference on the CPU
Discover how you can use BNNSGraph to accelerate the execution of your machine learning model on the CPU. We will show you how to use BNNSGraph to compile and execute a machine learning model on the CPU and share how it provides real-time guarantees such as no runtime memory allocation and single-threaded running for audio or signal processing models.
