Explain concurrency contexts
Asked on 2024-08-24
1 search
Concurrency contexts in Swift refer to the way tasks are managed and executed across different threads or queues in an application. In the context of migrating an app to Swift 6, concurrency is handled more explicitly and safely, thanks to Swift's concurrency model.
In the original app setup, concurrency was managed using multiple concurrent queues, including the main queue for UI and model work, a dispatch queue for background tasks, and arbitrary queues for certain callbacks. This setup could lead to confusion and potential data races, as it wasn't always clear which queue was executing code at any given time.
With Swift concurrency, the architecture becomes more organized. The main actor is used for UI views and models, ensuring that these components run on the main thread. Background operations are performed on dedicated actors, which helps in managing concurrency more predictably and safely.
Swift 6 introduces data race safety by default, turning potential data race issues into compile-time errors. This is achieved through mechanisms like actors for protecting mutable state and the Sendable protocol for safe data sharing. By enabling strict concurrency checking, developers can identify and resolve concurrency issues during development, reducing runtime errors and improving app stability.
For more detailed information on concurrency contexts and how to migrate your app to Swift 6, you can refer to the session Migrate your app to Swift 6 (08:53).
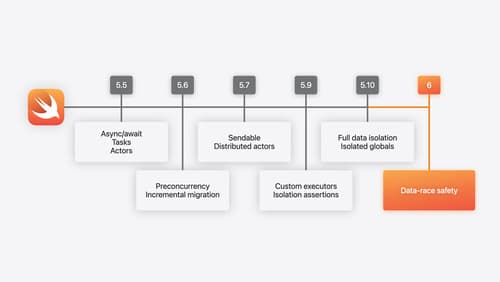
What’s new in Swift
Join us for an update on Swift. We’ll briefly go through a history of Swift over the past decade, and show you how the community has grown through workgroups, expanded the package ecosystem, and increased platform support. We’ll introduce you to a new language mode that achieves data-race safety by default, and a language subset that lets you run Swift on highly constrained systems. We’ll also explore some language updates including noncopyable types, typed throws, and improved C++ interoperability.
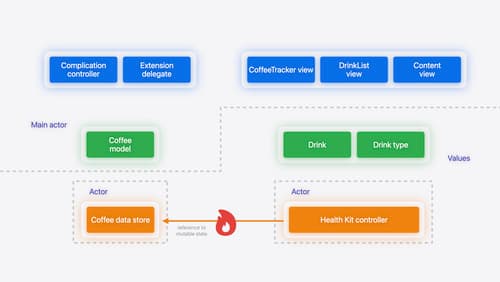
Migrate your app to Swift 6
Experience Swift 6 migration in action as we update an existing sample app. Learn how to migrate incrementally, module by module, and how the compiler helps you identify code that’s at risk of data races. Discover different techniques for ensuring clear isolation boundaries and eliminating concurrent access to shared mutable state.
