what is async?
Asked on 2024-09-06
1 search
Async, short for asynchronous, refers to a programming model that allows tasks to be executed without blocking the main thread. In Swift, this is achieved using the async and await keywords. An async function is one that can pause its execution to wait for a long-running task to complete, such as reading from a disk or waiting for a network response. This allows other tasks to use the CPU while the async task is waiting, improving the efficiency of resource usage.
When you call an async function, you use the await keyword to indicate that the function may suspend at that point. This model is particularly useful in scenarios where you want to perform non-blocking operations, such as handling HTTP requests in a server environment.
For more details, you can refer to the session A Swift Tour: Explore Swift’s features and design (19:10) where the async/await syntax in Swift is discussed.
A Swift Tour: Explore Swift’s features and design
Learn the essential features and design philosophy of the Swift programming language. We’ll explore how to model data, handle errors, use protocols, write concurrent code, and more while building up a Swift package that has a library, an HTTP server, and a command line client. Whether you’re just beginning your Swift journey or have been with us from the start, this talk will help you get the most out of the language.
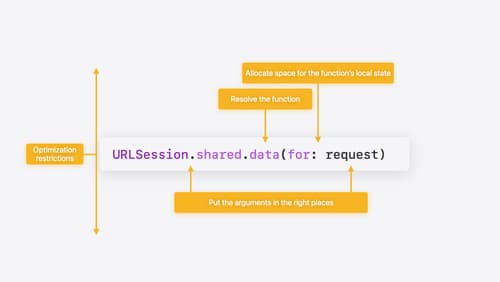
Explore Swift performance
Discover how Swift balances abstraction and performance. Learn what elements of performance to consider and how the Swift optimizer affects them. Explore the different features of Swift and how they’re implemented to further understand the tradeoffs available that can impact performance.
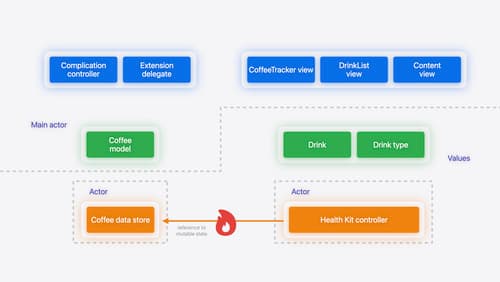
Migrate your app to Swift 6
Experience Swift 6 migration in action as we update an existing sample app. Learn how to migrate incrementally, module by module, and how the compiler helps you identify code that’s at risk of data races. Discover different techniques for ensuring clear isolation boundaries and eliminating concurrent access to shared mutable state.
