What is homomorphic encryption?
Asked on 2024-07-30
2 searches
Homomorphic encryption is a form of encryption that allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without needing to decrypt it first. This means that a server can process the encrypted data and return an encrypted result, which can then be decrypted by the client to reveal the final output. This technique ensures that sensitive data remains secure and private even while being processed.
In the context of WWDC, homomorphic encryption is mentioned in the session What’s new in privacy. It is used in the implementation of Live Caller ID, enabling a server to make use of an encrypted value without decrypting it, thus preserving user privacy. The server computes on the incoming ciphertext, evaluates for a match, and then returns the transformed ciphertext back to the requesting device, where the results are displayed. This allows for the implementation of live caller ID without revealing sensitive information such as an incoming phone number.
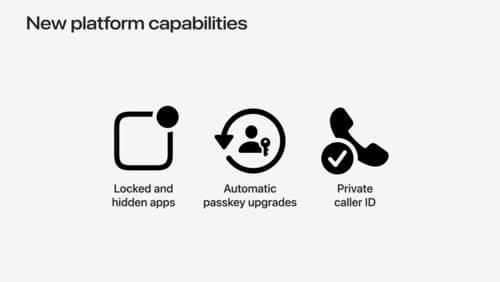
What’s new in privacy
At Apple, we believe privacy is a fundamental human right. Learn about new and improved permission flows and other features that manage data in a privacy-preserving way, so that you can focus on creating great app experiences.
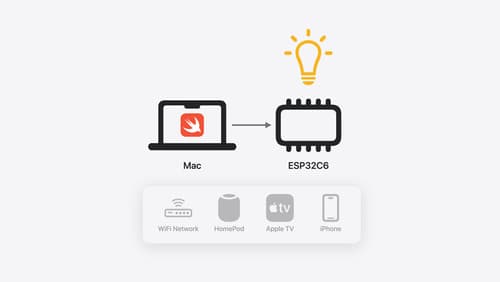
Go small with Embedded Swift
Embedded Swift brings the safety and expressivity of Swift to constrained environments. Explore how Embedded Swift runs on a variety of microcontrollers through a demonstration using an off-the-shelf Matter device. Learn how the Embedded Swift subset packs the benefits of Swift into a tiny footprint with no runtime, and discover plenty of resources to start your own Embedded Swift adventure.
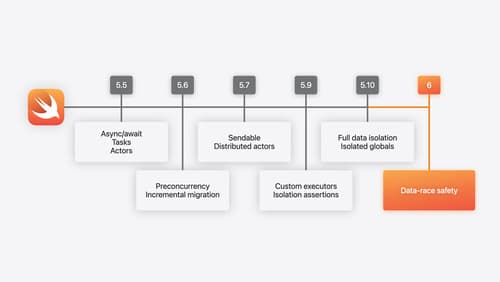
What’s new in Swift
Join us for an update on Swift. We’ll briefly go through a history of Swift over the past decade, and show you how the community has grown through workgroups, expanded the package ecosystem, and increased platform support. We’ll introduce you to a new language mode that achieves data-race safety by default, and a language subset that lets you run Swift on highly constrained systems. We’ll also explore some language updates including noncopyable types, typed throws, and improved C++ interoperability.
