closure
Asked on 2024-09-14
1 search
The concept of closures was discussed in several sessions at WWDC 2024. Here's a summary of the relevant information:
-
Analyze heap memory: This session discusses how Swift closures capture values and allocate memory on the heap to store these captures. Closures capture references strongly by default, which can lead to reference cycles. To break these cycles, you can use weak or unowned captures. The session also provides a practical example of resolving a reference cycle caused by a closure strongly capturing a thumbnail renderer, suggesting the use of a capture list to specify weak or unowned references. You can find more details in the chapter Resolving leaks of Swift closure contexts.
-
Explore Swift performance: This session explains how closures in Swift are passed around as values of function type, consisting of a function pointer and a context pointer. It also discusses the differences between non-escaping and escaping closures, particularly in terms of memory allocation and management. The chapter on Closures provides more insights into their performance implications.
-
Run, Break, Inspect: Explore effective debugging in LLDB: This session highlights the use of closures in debugging scenarios, particularly in declarative code like SwiftUI. It demonstrates how breakpoints can be used to pause execution inside closures to inspect program behavior. The chapter on Breakpoints might be useful for understanding how closures interact with debugging tools.
These sessions provide a comprehensive overview of how closures work in Swift, their impact on memory management, and how they can be effectively debugged.

Analyze heap memory
Dive into the basis for your app’s dynamic memory: the heap! Explore how to use Instruments and Xcode to measure, analyze, and fix common heap issues. We’ll also cover some techniques and best practices for diagnosing transient growth, persistent growth, and leaks in your app.
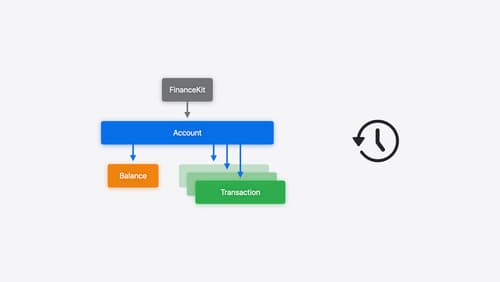
Meet FinanceKit
Learn how FinanceKit lets your financial management apps seamlessly and securely share on-device data from Apple Cash, Apple Card, and more, with user consent and control. Find out how to request one-time and ongoing access to accounts, transactions, and balances — and how to build great experiences for iOS and iPadOS.
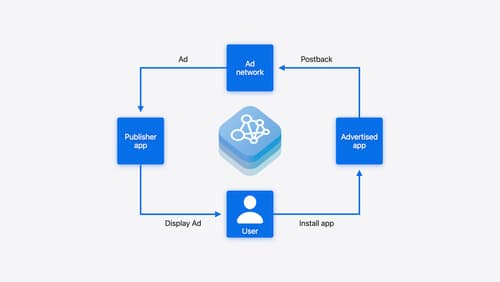
Meet AdAttributionKit
Introducing AdAttributionKit, a new iOS framework for privacy-preserving ad attribution. Learn how AdAttributionKit supports re-engagement, click-through attribution (including support for custom creative), JWS formatted impressions and postbacks, and more. We’ll provide insight into testing your AdAttributionKit implementation and deep-dive into code snippets and best practices for adopting AdAttributionKit.
