concurrency とは何ですか?
Asked on 2024-10-08
1 search
Concurrency in the context of Swift, as discussed in the WWDC sessions, refers to the ability to execute multiple tasks simultaneously, which can improve the performance and responsiveness of applications. Swift's concurrency model is designed to be safe and efficient, helping developers avoid common pitfalls like data races, which occur when multiple threads access shared data simultaneously and at least one of them modifies it.
Swift concurrency introduces several key concepts and tools:
-
Actors: These are used to protect mutable state and ensure that only one task can access the state at a time, preventing data races.
-
Async/Await: This feature allows developers to write asynchronous code that is easy to read and maintain. It helps manage tasks that can run concurrently without blocking the main thread.
-
Data Race Safety: Swift 6 introduces data race safety by default, turning potential data race issues into compile-time errors, which significantly enhances the security and reliability of applications.
-
Low-level Synchronization Primitives: These include atomics and mutexes, which provide efficient, lock-free implementations for safe concurrent access to shared data.
For more detailed information, you can refer to the sessions like Migrate your app to Swift 6 and What’s new in Swift, which cover Swift 6's concurrency features and data-race safety.
A Swift Tour: Explore Swift’s features and design
Learn the essential features and design philosophy of the Swift programming language. We’ll explore how to model data, handle errors, use protocols, write concurrent code, and more while building up a Swift package that has a library, an HTTP server, and a command line client. Whether you’re just beginning your Swift journey or have been with us from the start, this talk will help you get the most out of the language.
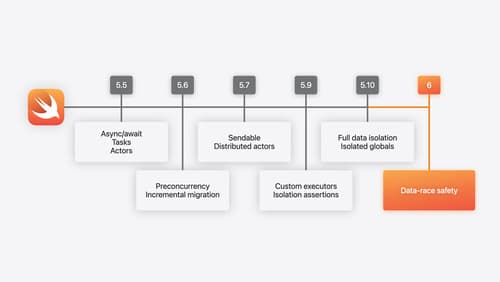
What’s new in Swift
Join us for an update on Swift. We’ll briefly go through a history of Swift over the past decade, and show you how the community has grown through workgroups, expanded the package ecosystem, and increased platform support. We’ll introduce you to a new language mode that achieves data-race safety by default, and a language subset that lets you run Swift on highly constrained systems. We’ll also explore some language updates including noncopyable types, typed throws, and improved C++ interoperability.
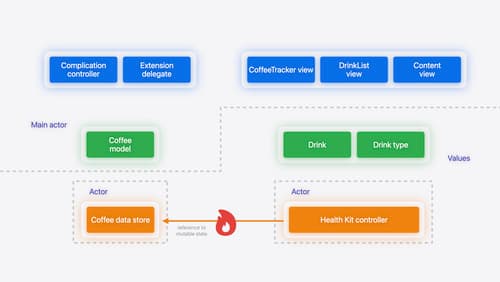
Migrate your app to Swift 6
Experience Swift 6 migration in action as we update an existing sample app. Learn how to migrate incrementally, module by module, and how the compiler helps you identify code that’s at risk of data races. Discover different techniques for ensuring clear isolation boundaries and eliminating concurrent access to shared mutable state.
