borrowing
Asked on 2025-06-15
1 search
The concept of "borrowing" in Swift is discussed in the context of ownership and memory management. Borrowing a value means asserting that nobody else can consume or mutate it, which is useful when you just want to read a value without altering it. This is a common practice when passing arguments, as it allows you to pass information without additional overhead. However, Swift sometimes needs to defensively copy arguments instead of borrowing them, especially in complex scenarios where it cannot guarantee that the value won't be mutated or consumed elsewhere.
For more details, you can refer to the session "Explore Swift performance" where borrowing is discussed in the context of Swift's ownership system. You can find this discussion in the chapter on Value copying.
Additionally, the session "Consume noncopyable types in Swift" also touches on borrowing in the context of noncopyable types, explaining how borrowing provides read access similar to a let binding. This is covered in the chapter on Noncopyable Types.
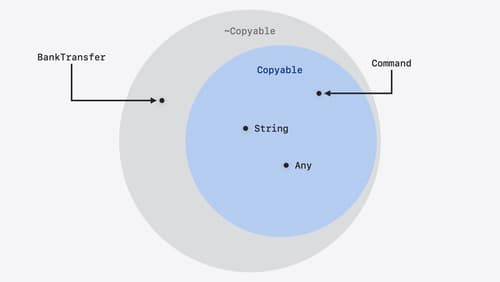
Consume noncopyable types in Swift
Get started with noncopyable types in Swift. Discover what copying means in Swift, when you might want to use a noncopyable type, and how value ownership lets you state your intentions clearly.
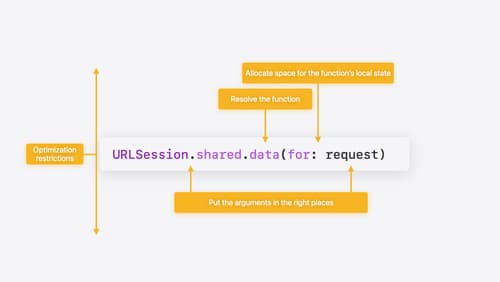
Explore Swift performance
Discover how Swift balances abstraction and performance. Learn what elements of performance to consider and how the Swift optimizer affects them. Explore the different features of Swift and how they’re implemented to further understand the tradeoffs available that can impact performance.
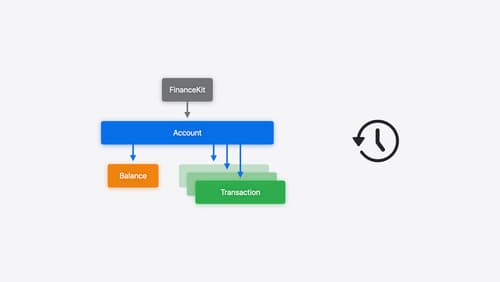
Meet FinanceKit
Learn how FinanceKit lets your financial management apps seamlessly and securely share on-device data from Apple Cash, Apple Card, and more, with user consent and control. Find out how to request one-time and ongoing access to accounts, transactions, and balances — and how to build great experiences for iOS and iPadOS.
